Herbs are the leaves of plants, and spices are the roots, bark, and seeds (anything that is not a leaf). Adding herbs and spices into cooking goes beyond adding flavor; they add surprising protective health benefits.
Herbs and spices are some of the most anti-inflammatory foods because they are packed with antioxidants! For instance, researchers found that cloves, ginger, rosemary, and (unheated) turmeric reduced the inflammation caused by LDL (bad) cholesterol (Percival at al., 2012). Experts studied the antioxidative activity of 3,100 foods, including 425 dried and ground spices. They concluded herbs and spices ounce per ounce have some of the greatest antioxidant activities known (Carlsen et al., 2010).
For example, cloves have the highest mean antioxidant value of all foods (277.3 mmol/100g), followed by peppermint (116.4), allspice (100.4), cinnamon(77), oregano(63.2), thyme(56), sage(44.3), rosemary(44.8), and saffron(44.5). To put this into perspective, chicken, beef, and bacon score up to 1.0 mmol/100g.
What are antioxidants?
Imagine you have an apple, and then you slice the apple into eight parts using an apple slicer. For four of the slices, you put lime juice on it. The other four slices don’t. With time, what do you think will happen with the apple slices you didn’t put the lime juice on? That’s right; they will brown, they will deteriorate. That is called oxidation. The other apple slices will not oxidate. Why? Because lime juice contains protective components called antioxidants. It protected the apple cells against oxidation!
Image credit: Rebecca Elliott
Antioxidants and our health
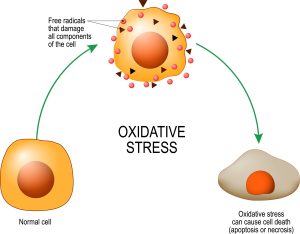
Oxidation not only affect the apple cells in the exemple above, it also affects our cell membranes and even our DNA. Moreover, it is linked to different chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and cognitive decline, among others (Harvard, n.a). See the illustration below:
Image Credit: Getty Images
We only find antioxidants in plants (especially herbs and spices). In the same way the antioxidants in lime juice protect the apple cells, antioxidants in herbs and spices can preserve our cell membranes and DNA against oxidative stress and disease.
If you are interested in learning HOW to include more herbs and spices in cooking, please read the other blogs in this series.
References
Harvard T.H. Chan, School of Public Health. (n.a.). Antioxidants. Retrieved from https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/antioxidants/
Carlsen, M. H., Halvorsen, B. L., Holte, K., Bøhn, S. K., Dragland, S., Sampson, L., Willey, C., Senoo, H., Umezono, Y., Sanada, C., Barikmo, I., Berhe, N., Willett, W. C., Phillips, K. M., Jacobs, D. R., Jr, & Blomhoff, R. (2010). The total antioxidant content of more than 3100 foods, beverages, spices, herbs and supplements used worldwide. Nutrition journal, 9, 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-9-3
S. S. Percival, J. P. V. Heuvel, C. J. Nieves, C. Montero, A. J. Migliaccio, J. Meadors. Bioavailability of Herbs and Spices in Humans as Determined by ex vivo Inflammatory Suppression and DNA Strand Breaks. J Am Coll Nutr. 2012 31(4):288 – 294.
Source: UF/IFAS Pest Alert
Note: All images and contents are the property of UF/IFAS.